Modern missile technology has evolved into three dominant categories – cruise missiles, hypersonic missiles, and ballistic missiles. Each serves distinct military purposes with unique flight characteristics, speeds, and capabilities. This comparison breaks down their differences in performance, propulsion, and strategic applications.
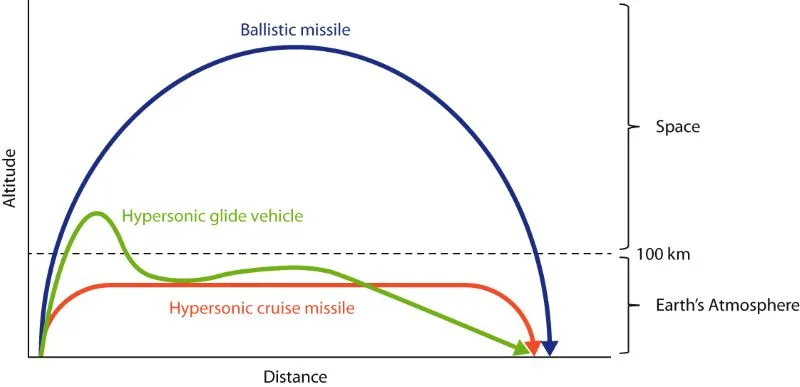
1. Speed & Flight Trajectory Comparison
| Feature | Cruise Missile | Hypersonic Missile | Ballistic Missile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Subsonic to Supersonic (Mach 0.8-3) | Hypersonic (Mach 5+) | Hypersonic (Mach 5-20+) |
| Flight Altitude | Low-altitude (terrain-hugging) | Variable (low to high) | High (exo-atmospheric) |
| Trajectory | Aerodynamic, controlled flight | Glide or cruise at high speed | Parabolic (space-reentry) |
| Maneuverability | High (can adjust path) | Extreme (evasive maneuvers) | Low (fixed trajectory) |
2. Propulsion & Guidance Systems
Cruise Missiles
Propulsion: Turbojet/ramjet engines
Guidance: GPS, TERCOM, INS, infrared
Range: 300-2,500 km
Examples: Tomahawk (USA), BrahMos (India-Russia)
Hypersonic Missiles
Propulsion: Scramjet (air-breathing) or boost-glide
Guidance: Advanced radar/IR + AI-assisted
Range: 500-5,000+ km
Examples: Avangard (Russia), DF-ZF (China), AGM-183A (USA)
Ballistic Missiles
Propulsion: Multi-stage rockets
Guidance: Inertial + terminal homing
Range: Short-range (SRBM) to ICBM (15,000 km)
Examples: Minuteman III (USA), Shaheen-III (Pakistan), Agni-V (India)
3. Strategic Advantages & Disadvantages
| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Cruise Missile | ✔ Stealthy & precise ✔ Low-altitude evasion | ✖ Slow speed ✖ Vulnerable to air defenses |
| Hypersonic Missile | ✔ Near-impossible interception ✔ High-speed precision strike | ✖ Complex & expensive ✖ Limited payload capacity |
| Ballistic Missile | ✔ Extreme range & speed ✔ Large payload capacity | ✖ Predictable trajectory ✖ Detectable by early-warning systems |
4. Defense & Countermeasures
Cruise Missiles: Shot down by fighter jets, SAMs (Patriot, S-400)
Hypersonic Missiles: Extremely hard to intercept (lasers/railguns in development)
Ballistic Missiles: Intercepted by ABM systems (THAAD, Aegis)
5. Future of Missile Technology
Hypersonic dominance: Major powers (USA, Russia, China) investing heavily
AI-guided swarms: Autonomous cruise missile clusters
Space-based interceptors: Anti-ballistic missile satellites
Ballistic Missile vs Cruise Missile
| Features | Ballistic Missile | Cruise Missile |
| Flight Path | Follows a parabolic trajectory; most of its flight is outside the atmosphere. | Flies within the Earth’s atmosphere, following a relatively straight or guided path. |
| Propulsion | Powered during the initial phase of launch; relies on gravity and momentum for most of the flight. | Powered throughout its flight using jet engines or turbojets. |
| Speed | Typically faster; can reach hypersonic speeds. | Slower compared to ballistic missiles; subsonic or supersonic speeds. |
| Guidance System | Primarily inertial guidance; less manoeuvrable in the mid-course phase. | Highly manoeuvrable with advanced guidance systems like GPS or terrain-following radar. |
| Range | Generally long-range, capable of intercontinental distances (ICBMs). | Typically medium to short-range, though some have long-range capabilities. |
| Accuracy | Less accurate compared to cruise missiles; used for large-scale destruction. | High precision; designed for targeted strikes. |
| Payload Type | Can carry nuclear, conventional, or other payloads; often used for strategic missions. | Can carry conventional or nuclear payloads; suited for tactical missions. |
| Detection | Easier to detect during the boost phase due to heat and smoke trails. | Harder to detect due to low altitude flight and terrain hugging capabilities. |
| Examples | Prithvi I, Prithvi II, Agni I, Agni II and Dhanush missiles | BrahMos Missile |
Conclusion
While ballistic missiles remain key for nuclear deterrence, hypersonic missiles are reshaping modern warfare with unmatched speed and evasion. Cruise missiles still excel in precision strikes, but their slower speed makes them vulnerable. The future battlefield will likely see a mix of all three, with hypersonics leading the next arms race.
Refernces
