As of January 20, 2025, the Indian government has not officially constituted the 8th Pay Commission. However, various projections and discussions have emerged regarding potential changes to the salary pay matrix for central government employees.
how fitment factor is decided?
it is determined by considering various factors such as inflation, employee needs, and the government’s financial capacity.
if the current basic pay is ₹18,000 and the revised basic pay is ₹51,480, the fitment factor would be 2.86 (₹51,480 ÷ ₹18,000).
rrc group d 8th cpc expected salary with 1.92 fitment factor
fitment factor = Basic Pay + DA
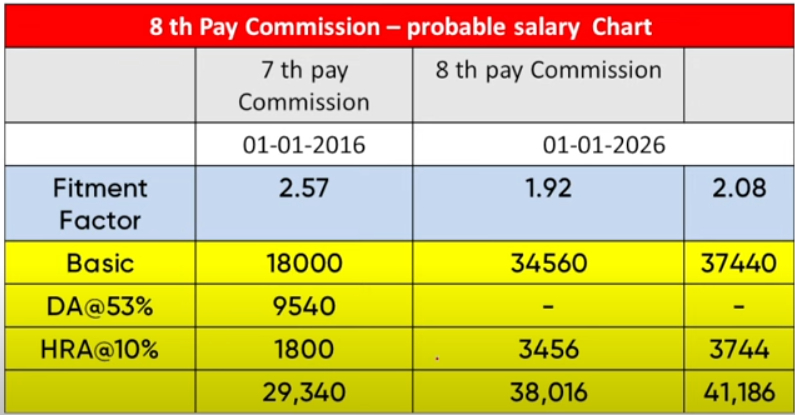
8th Pay Commission Expected fitment factor based on 7th CPC railway group d
2016 : DA 125%+Basic 100% = 2.25X then fitment facotr 2.57
2026: DA 60% 1.6x then fitment factor 1.9 or 2
8th Pay Commission: Expected Salary Hike Across Levels fitment factor of 2.86
Based on the anticipated fitment factor of 2.86 under the 8th CPC, the expected revised basic pay for each level in the Pay Matrix of central government employees is as follows:
18000*2.86=51480
| Level 1 | ₹18,000 | ₹51,480 | ₹33,480 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 2 | ₹19,900 | ₹56,914 | ₹37,014 |
| Level 3 | ₹21,700 | ₹62,062 | ₹40,362 |
| Level 4 | ₹25,500 | ₹72,930 | ₹47,430 |
| Level 5 | ₹29,200 | ₹83,512 | ₹54,312 |
| Level 6 | ₹35,400 | ₹1,01,244 | ₹65,844 |
| Level 7 | ₹44,900 | ₹1,28,414 | ₹83,514 |
| Level 8 | ₹47,600 | ₹1,36,136 | ₹88,536 |
| Level 9 | ₹53,100 | ₹1,51,866 | ₹98,766 |
| Level 10 | ₹56,100 | ₹1,60,446 | ₹1,04,346 |
| pay level | 7th | 8th | growth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | ₹18,000 | ₹51,480 | ₹33,480 | |
| Level 2 | ₹19,900 | ₹56,914 | ₹37,014 | |
| Level 3 | ₹21,700 | ₹62,062 | ₹40,362 | |
| Level 4 | ₹25,500 | ₹72,930 | ₹47,430 | |
| Level 5 | ₹29,200 | ₹83,512 | ₹54,312 | |
| Level 6 | ₹35,400 | ₹1,01,244 | ₹65,844 | |
| Level 7 | ₹44,900 | ₹1,28,414 | ₹83,514 | |
| Level 8 | ₹47,600 | ₹1,36,136 | ₹88,536 | |
| Level 9 | ₹53,100 | ₹1,51,866 | ₹98,766 | |
| Level 10 | ₹56,100 | ₹1,60,446 | ₹1,04,346 |
Projected 8th Pay Commission Pay Matrix:
Based on available analyses, the following table outlines the anticipated changes in the basic salary across different pay levels:
| Pay Matrix Level | 7th CPC Basic Salary (₹) | Projected 8th CPC Basic Salary (₹) |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 18,000 | 21,600 |
| Level 2 | 19,900 | 23,880 |
| Level 3 | 21,700 | 26,040 |
| Level 4 | 25,500 | 30,600 |
| Level 5 | 29,200 | 35,040 |
| Level 6 | 35,400 | 42,480 |
| Level 7 | 44,900 | 53,880 |
| Level 8 | 47,600 | 57,120 |
| Level 9 | 53,100 | 63,720 |
| Level 10 | 56,100 | 67,320 |
| Level 11 | 67,700 | 81,240 |
| Level 12 | 78,800 | 94,560 |
| Level 13 | 1,23,100 | 1,47,720 |
| Level 13A | 1,31,100 | 1,57,320 |
| Level 14 | 1,44,200 | 1,73,040 |
| Level 15 | 1,82,200 | 2,18,400 |
| Level 16 | 2,05,400 | 2,46,480 |
| Level 17 | 2,25,000 | 2,70,000 |
| Level 18 | 2,50,000 | 3,00,000 |
These projections suggest a potential increase in the minimum basic salary from ₹18,000 to ₹21,600.
Fitment Factor:
The fitment factor is a crucial component in determining the revised salaries under the new pay commission. It is applied to the existing basic pay to arrive at the new basic pay. While some sources anticipate a fitment factor of 2.28,
others suggest it could be as high as 2.86.
This means that the current basic pay would be multiplied by the fitment factor to determine the revised salary.
Implementation Timeline:
Historically, pay commissions in India are set up every 10 years. The 7th Pay Commission was implemented on January 1, 2016. Following this pattern, the 8th Pay Commission is anticipated to be implemented around January 1, 2026. However, as of now, no official announcement has been made regarding its constitution or implementation.
8th Pay Commission: Minimum Pension For Central Govt Employees Under UPS
Similarly, pensions are expected to experience a significant hike, increasing from the current Rs 9,000 to a range between Rs 17,280 and Rs 25,740, depending on the finalized fitment factor.
The Pay Matrix covers a wide range of positions, each aligned to specific levels:
Level 1: Peons, Attendants, MTS (Multi-Tasking Staff) performing essential support tasks.
Level 2: Lower Division Clerks (LDCs) managing clerical and routine administrative duties.
Level 3: Constables and Skilled Trades Staff in police, defense, or public services.
Level 4: Stenographers (Grade D) and Junior Clerks managing transcription and documentation.
Level 5: Senior Clerks, Assistants, or Technical Staff providing higher-level administrative or technical support.
Level 6: Inspectors, Sub-Inspectors, and Junior Engineers (JEs) in technical or supervisory roles.
Level 7: Superintendents, Section Officers, or Assistant Engineers (AEs) handling project management or complex administrative tasks.
Level 8: Senior Section Officers or Assistant Audit Officers, managing audits or higher administrative functions.
Level 9: Deputy Superintendents of Police (DSPs) or Accounts Officers, responsible for operational or financial management.
Level 10: Group A Officers, such as Assistant Commissioners or entry-level officers in services like IAS, IPS, and IFS.